Bartonellosis
February 8, 2016
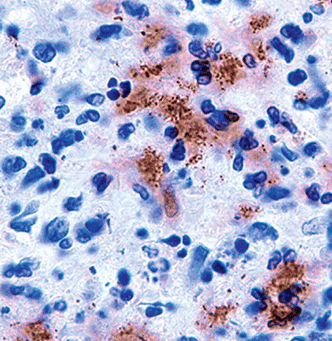
Members of the Bartonella genus are Gram-negative rod shaped bacteria that live exclusively inside cells. Bartonella is transmitted via fleas, lice, sand flies, cat scratches, and ticks. Bartonella henselae, the most commonly identified member of the genus, is the causative agent of cat scratch disease. As its name suggests, this disease is often caused by the scratch of a cat; however, it may also be transmitted by ticks and fleas.
Symptoms of Bartonella infection include fever, enlarged lymph nodes, fatigue, headaches, rash, bone pain, and involvement of the heart valve. Culturing an infected heart valve often produces negative results. Less commonly, encephalopathy and inflammation of the retina and optic nerve are observed. Immuno-compromised individuals may experience subcutaneous skin and bone lesions as well as lesions of the liver and spleen.
Diagnosis of Bartonella is based on a clinical history and confirmatory serological tests. The preferred treatment for the disease is antibiotics.




