Ehrlichiosis
February 8, 2016
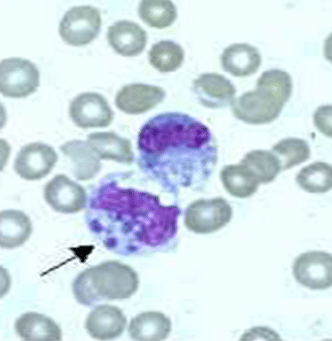
Ehrlichiosis is a general term used to describe several bacterial diseases that affect humans and animals. Members of the Ehrlichia genus are Gram-negative, rod shaped bacteria that live inside white blood cells. The lone star tick is the primary vector of this disease, although the Ixodes tick is also a known vehicle of transmission. For this reason, people with Lyme disease may also be co-infected with ehrlichiosis.
Ehrlichia chaffeensis and Ehrlichia ewingii are the two most commonly implicated species in human disease. Symptoms of the infection take between one to two weeks to appear and include fever, headaches, chills, malaise, vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, confusion, muscle pain, and red eyes. The absence of a rash can help to distinguish ehrlichiosis clinically from Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever.
Ehrlichia is diagnosed based on a combination of clinical signs, symptoms, and confirmatory lab test. Antibiotics are the treatment of choice.




